Socioeconomic impacts
Socioeconomic impacts
Prior to the onset of COVID-19, youth (aged 15 to 24) were already three times more likely to be unemployed compared to adults, while 126 million young workers were in extreme and moderate poverty worldwide (International Labour Organization, 2020). Young workers are also more likely to be in precarious employment than other age groups. Whereas some 77 per cent of youth are estimated to be informally employed globally, this percentage is even higher for young women in low and lower-middle-income countries (International Labour Organization, 2018).
The increase in unemployment as a result of COVID-19 is expected to exceed the rise in rates of unemployment in the aftermath of the 2009 global financial crisis. Based on the 2009 experience, without targeted policy intervention, it is likely that youth will again be disproportionately affected by a global recession, with a higher percentage of young people being unemployed compared to adults, and a slower uptake of employment by young people during the recovery. In light of the threat to the livelihoods of many youth, it is crucial that measures to ease the financial impacts on households are comprehensive and sufficient to bridge the gap resulting from loss of earnings.
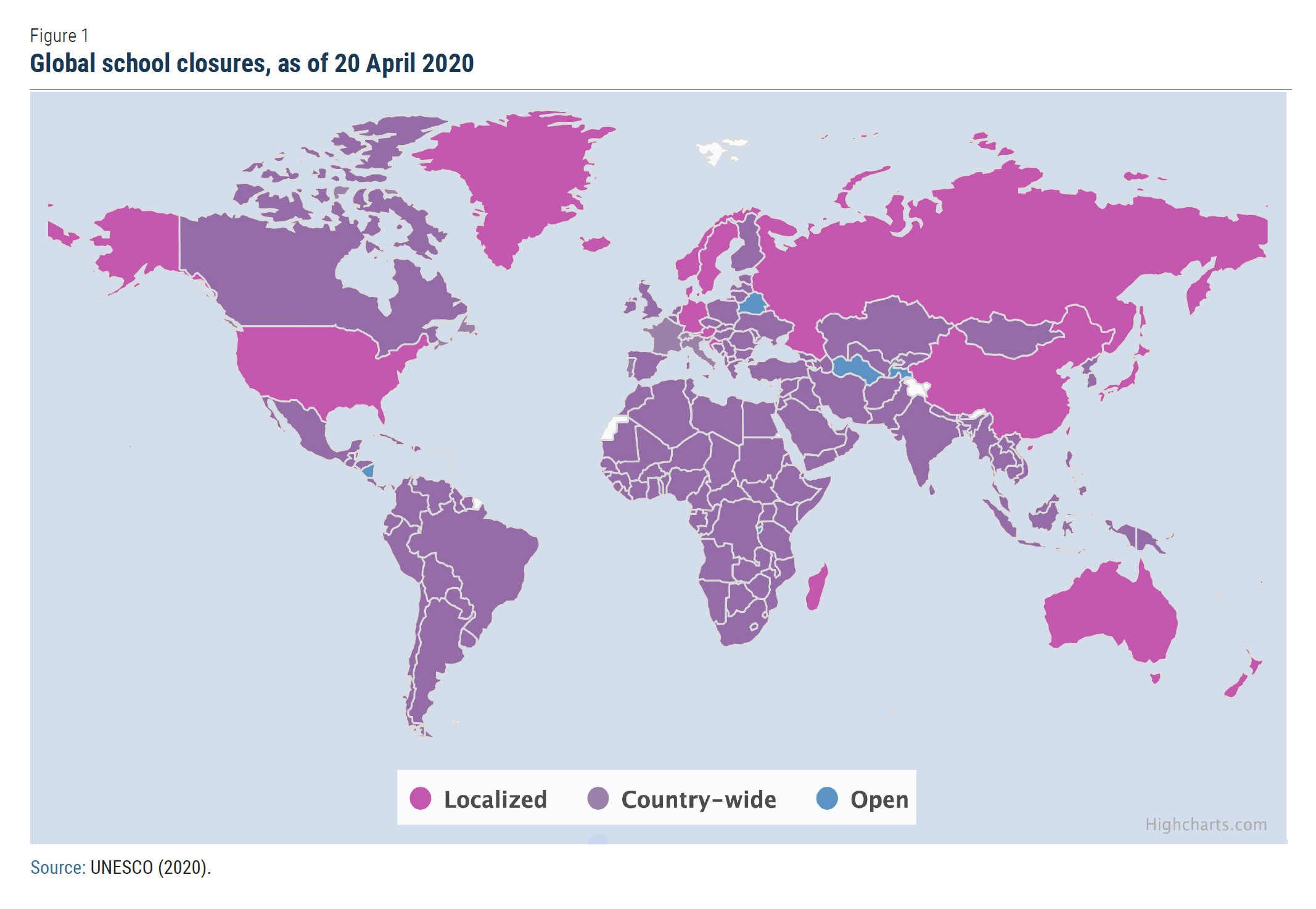
The global pandemic is also having an unprecedented impact on education systems all over the world, with far-reaching social consequences. According to UNESCO (2020), so far 191 countries have implemented nationwide or localized school closures, resulting in over 91 per cent of enrolled students, or 1.5 billion people, not being able to go to school (Figure 1). These students face disruptions to their education of uncertain duration, with varying levels of alternative delivery methods. These disruptions can negatively impact learning, access to nutrition, and consequently, graduation rates. School closures have a particularly adverse effect on poorer students, students without stable internet access at home, and children relying on help from their schools in meeting their nutrition and health needs. The situation is especially acute for girls and young women who are disproportionately excluded from education.
To alleviate the situation, governments should ensure there is continuity in learning by promoting high-tech, low-tech and no-tech solutions. Given the large digital divide that exists, solutions such as delivering text-based content via cellular networks rather than videoconferencing that relies on high-speed internet, and paper-based distance learning materials for families without any digital connectivity access should also be considered. Students with special needs, such as those with disabilities, will require additional attention and support as remote learning pose particular challenges for them and their families.
Vulnerable and marginalised youth are at particular risk of COVID-19 and its impacts. Young migrants and refugees, youth living in rural areas, adolescent girls and young women, indigenous and ethnic minority youth, young persons with disabilities, young people living with HIV/AIDS, young people of different sexual orientations and gender identities, and homeless youth already experience challenges in accessing healthcare services and social protection. Young people with physical or mental health conditions also face an elevated risk in relation to COVID-19. Many young people may not have stable housing and therefore cannot safely engage in home-based social distancing. The pandemic and economic recession may further fuel stigma and discrimination against certain groups of young people, which in turn would further exclude them from accessing healthcare and maintaining their livelihoods. These disparate impacts should inform the comprehensive policy response to this crisis.
Social policy responses
Social protection measures such as cash transfer payments, unemployment support, paid sick leave, and access to healthcare are being expanded in some jurisdictions on a temporary basis. If such measures are to “leave no one behind,” it is crucial that they take into account the particular concerns and needs of young people, especially those who are not included in family-based disbursements or employment-based social protection systems, such as those with informal jobs or in the gig economy. The policies implemented during a crisis should not only safeguard the livelihoods and financial security of youth in the short term, but also serve as the basis for building resilient social safety nets that reduce the vulnerability of young people in the long term.
Expanding access to healthcare has been a critical aspect of the COVID-19 response. In situations where healthcare coverage is linked to employment, young people experience barriers to access as they are disproportionately unemployed, work in the informal sector or are among the working poor. Services targeting the needs of young women and girls have been, in some cases, disrupted or have had their resources diverted. It is a right of all persons to have access to and have the highest attainable standards of health (United Nations, 1966). As the virus can affect and be transmitted by everyone, the COVID-19 pandemic also underscores the extent to which universal health coverage is of paramount societal interest. To ensure effective access to healthcare for all young people during this time, long-recognized structural barriers, such as those posed by language or by facilities that are inaccessible to persons with disabilities, must now be dismantled. The COVID-19 pandemic makes clear the extent to which such barriers not only negatively affect the health of those who are excluded from healthcare, but also imperil the public health response required to interrupt the transmission of the virus.
The ongoing crisis and mitigation measures also have implications for mental health. Many young people with mental health conditions are experiencing a deterioration of their health status. Prolonged social isolation and stress are expected to increase the incidences of young people with mental health conditions (Lee, 2020). Mental health therefore should be integrated as part of the broader health response. There may be longer term mental health impacts that are currently unknown, to which public service providers should be sensitive.
In many countries, years of austerity measures have left public services underfunded and weakened national responses to effectively address COVID-19. This should serve as a lesson in terms of the policy response to the pandemic. COVID-19 will likely stretch expenditures of governments and the corresponding deep recession will dramatically shrink fiscal revenues. Many governments are currently making extraordinary interventions to protect their economies. Similar investments are required to address both the immediate social impacts of COVID-19, including in relation to education and employment for youth, as well as the longer-term impacts on social development. Now is not the time to dial back investments in youth. The future economic recovery and the achievement of the SDGs will rely on skilled and healthy young people contributing with their labour, ideas and expertise.
Youth policy responses
The World Programme of Action for Youth (WPAY) calls on governments to ensure that their services meet the needs of young people. Under the current circumstances, it is especially important that youth are heard alongside other community voices in the rollout of health and non-health interventions in response to COVID-19.
Building up the capacity of youth to be able to make their own decisions and to take responsibility for their own health is a key element of the WPAY. Health education, public health promotion and evidence-based information are critical in combating the spread and effects of COVID-19. The role of governments as well as youth organisations and community groups will be essential to challenge the spread of disinformation online and to ensure that trustworthy public health information is disseminated. Young people themselves are also spreading public health information in engaging ways such as videos to promote effective handwashing or explain how social distancing can save lives in their communities.
Young innovators are already responding to the pandemic through projects with social impact. Around the world, governments and the private sector are partnering with young people to launch initiatives that leverage young people’s efforts to support their communities. Through voluntary initiatives, many young people have also supported vulnerable members of their community, for example in the distribution of groceries and medicines. Youth-driven innovation hubs, from Nigeria to New York, are supporting start-ups to develop technological solutions to address COVID-19, as the pandemic shifts more and more activities online. Policies that enable partnerships with young people in this area can deliver future economic dividends and provide an avenue for youth to contribute and demonstrate their solidarity in a time of crisis.
As the crisis unfolds, there will be a diverse range of youth policy responses that are tailored to specific contexts and needs. Countries should invest in protecting all human rights, going beyond the right to health, towards building a more resilient society, including for youth. Policies, particularly those that include coercive measures or subject certain persons to elevated risks, should be evidence-based, proportionate and non-discriminatory. Decisions regarding children below the age of 18 should always be made in the best interests of the child in line with the Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Conclusion and recommendations
In a little over five months, COVID-19 has morphed from a small outbreak to a pandemic, which the World Health Organization (WHO) deems a public health emergency of international concern. The accompanying socioeconomic crisis is so large in scope that the Secretary-General of the United Nations has described it as the biggest challenge the world has faced since World War II. The risk that this crisis poses to health, socioeconomic wellbeing and political instability cannot be underestimated by governments.
This crisis calls for global solutions, inter-generational solidarity and innovative, inclusive policy solutions. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development should guide the response to and recovery from this pandemic, and provide the framework for building the resilience and social cohesion that the world will need to combat future pandemics. The following policy recommendations are put forward for the consideration of the Member States and United Nations entities:
- Provide universal health coverage, including for all young persons, and ensure that health systems effectively meet the needs of youth in the time of COVID-19 and throughout the recovery phase, including public health promotion, testing and treatment, and provision of mental health services.
- Promote accurate public health information through various communication tools and empower young people to make evidence-based decisions regarding their health, while also proactively contributing to prevention and mitigation.
- Maintain or increase funding and investments in young people’s health, education and skills development, entrepreneurship, and expand their employment opportunities, improve work conditions, and enhance their civic participation.
- Adapt the delivery of education, through digital and non-digital methods from early childhood to tertiary education to ensure continued skills acquisition and learning, with particular attention to the needs of young women and girls.
- Develop policies that reach vulnerable and marginalised youth, including migrants and refugees, youth living in rural areas, adolescent girls and young women, indigenous and ethnic minority youth, young persons with disabilities, young people living with HIV/AIDS, young people of different sexual orientations and gender identities, and homeless youth.
- Strengthen national capacities to collect, analyse and disseminate data disaggregated by age, gender and other population characteristics, especially for addressing the most marginalized and vulnerable youth groups during and after this pandemic.
- Ensure that social protection systems include all young people, with special attention to those who are not covered by current social protection measures.
- Consult and engage youth in the development of health, economic and social interventions in response to COVID-19 and in its recovery.
- Promote innovation by youth for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, and the management of its corollary socioeconomic impacts.
- Respect, promote and protect the human rights of young people, including the right to non-discrimination.
References
International Labour Organization (2018). Women and Men in the Informal Economy: A Statistical Picture. Available from https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---dgreports/---dcomm/documents/publication/wcms_626831.pdf.
International Labour Organization (2020). Global Employment Trends for Youth 2020. Available from https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---dgreports/---dcomm/---publ/documents/publication/wcms_737648.pdf.
Lee, J. (2020). Mental health effects of school closures during COVID-19. The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health. April. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30109-7
UNESCO (2020). COVID-19 Educational Disruption and Response. Available from https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
United Nations (1966). International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, Article 12. General Assembly resolution 2200A (XXI).
 Welcome to the United Nations
Welcome to the United Nations